The Swiss Alps, renowned for their breathtaking beauty and majestic peaks, are not just a stunning landscape but also a geological marvel. Their formation is a result of millions of years of tectonic activity, erosion, and climatic changes. This article delves into the processes that led to the creation of the Swiss Alps, exploring the geological history and key events that shaped this iconic mountain range.
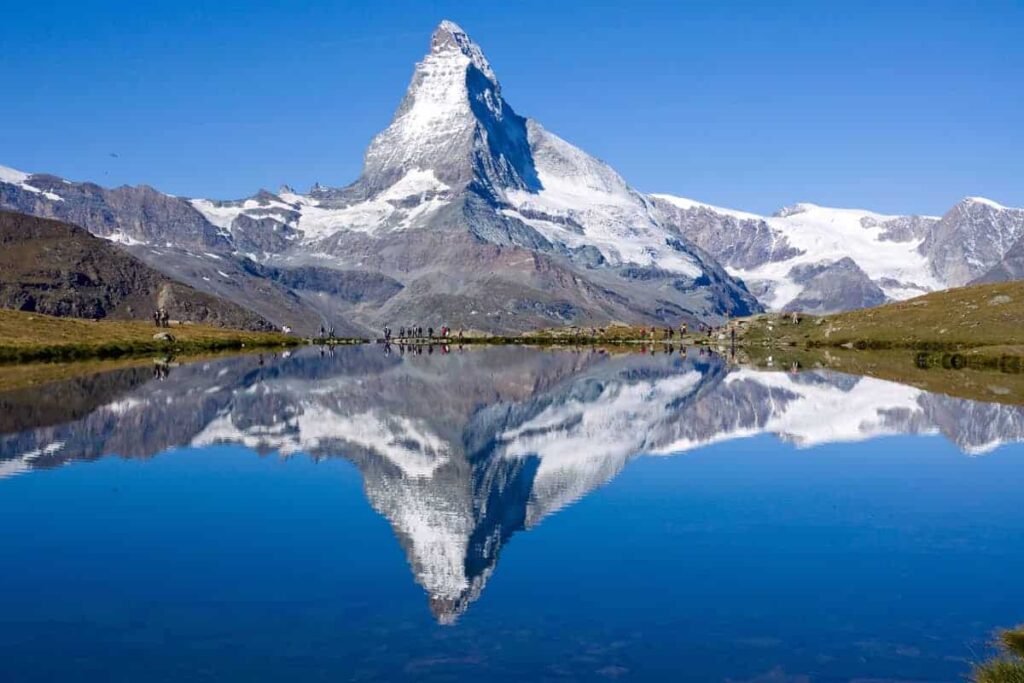

1. Geological Background of the Swiss Alps
– The Earth’s Crust and Plate Tectonics
The Earth’s crust is made up of several tectonic plates that float on the semi-fluid mantle beneath them. The movement of these plates is responsible for many geological phenomena, including the formation of mountain ranges. The Swiss Alps are primarily located at the convergence of the African and Eurasian tectonic plates, where immense geological forces have been at work for millions of years.
– The Tectonic History
The formation of the Swiss Alps can be traced back to the Mesozoic era, approximately 250 million years ago. During this period, the region that is now the Alps was covered by a vast sea known as the Tethys Ocean. The sedimentary layers deposited in this ocean later became the building blocks of the mountain range.
2. The Formation Process
– The Collision of Plates
Around 65 million years ago, during the Late Cretaceous period, the African plate began to collide with the Eurasian plate. This collision created immense pressure and led to the folding and uplift of the sedimentary layers that had accumulated in the Tethys Ocean. As a result, the once-flat seabed began to rise, giving birth to the early forms of the Alps.
– Folding and Faulting
The intense pressure from the colliding plates caused significant geological folding and faulting. The layers of sedimentary rock, including limestone, shale, and sandstone, were pushed upwards and deformed. This process created the distinct peaks and valleys characteristic of the Swiss Alps. The layers were also thrust over one another, leading to the formation of complex geological structures.
– Erosion and Weathering
Once the mountains had formed, erosion began to shape their current appearance. Glacial and river erosion played a crucial role in carving the valleys and peaks we see today. During the last Ice Age, which ended about 12,000 years ago, glaciers advanced and retreated across the Alps, further sculpting the landscape. The grinding action of glaciers eroded the rock, creating U-shaped valleys, sharp ridges, and stunning features like cirques and aretes.
3. The Role of Glaciation
– The Last Ice Age
The most significant impact on the Swiss Alps’ current topography occurred during the Pleistocene epoch (about 2.6 million to 11,700 years ago). The last Ice Age saw extensive glaciation in the region, with massive ice sheets covering large portions of the Alps. The movement of glaciers reshaped the landscape, deepening valleys and creating numerous lakes, such as Lake Geneva and Lake Lucerne.
– Glacial Retreat
As the climate warmed and the glaciers began to retreat, they left behind a transformed landscape. The sediment and debris deposited by the glaciers contributed to the formation of moraines and other glacial features, adding to the unique geological makeup of the region. The meltwater from the glaciers also shaped river systems and contributed to the lush valleys found in the Swiss Alps today.
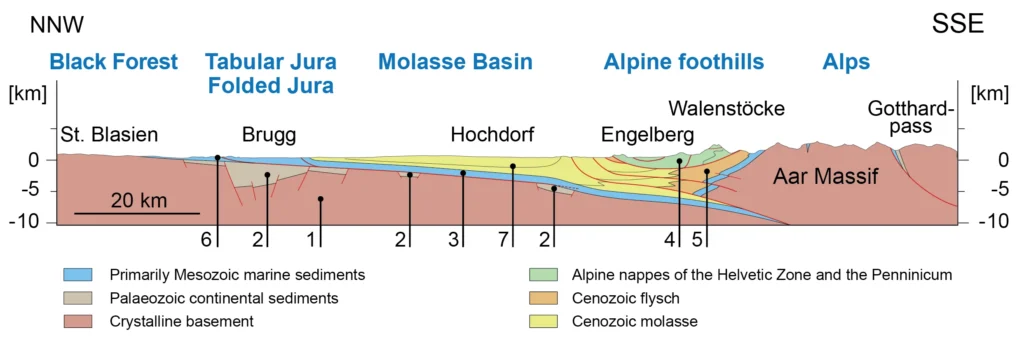
4. Ongoing Geological Activity
– Seismic Activity
The Swiss Alps are still tectonically active, and minor earthquakes are not uncommon. The ongoing movement of the African and Eurasian plates continues to exert pressure on the region, leading to occasional geological shifts. This activity can cause landslides and other geological phenomena, reminding us that the Alps are still evolving.
– Climate Change
In recent years, climate change has posed a new threat to the Swiss Alps. Warming temperatures have led to the retreat of glaciers, affecting the landscape and ecosystems. The loss of glaciers can impact the water supply for surrounding regions and alter the natural balance of the mountain environment.
Swiss Alps – Beauty of Switzerland
The formation of the Swiss Alps is a testament to the dynamic nature of our planet. From the collision of tectonic plates to the sculpting power of glaciers, the Alps have undergone a remarkable transformation over millions of years. Today, they stand as one of the most iconic mountain ranges in the world, attracting millions of visitors who come to marvel at their beauty and experience their majestic landscapes. Understanding the geological processes that shaped the Swiss Alps not only enhances our appreciation for this natural wonder but also highlights the ongoing changes that continue to shape our planet.




