The Netherlands is renowned for its intricate network of canals, which have played a crucial role in the country’s history, economy, and culture. The Dutch mastery of water management, exemplified by its canals, is a testament to the nation’s ingenuity in adapting to its unique geographical challenges. This article explores the history of canals in the Netherlands, their significance, and their lasting impact on Dutch society.

1. Historical Background of the Canals in the Netherlands
– Geographical Context
The Netherlands is a low-lying country with approximately one-third of its land situated below sea level. The Dutch have historically faced the dual challenges of managing water from the North Sea and the numerous rivers that flow through the region, including the Rhine, Meuse, and Scheldt. To combat flooding and reclaim land from the sea, the Dutch developed advanced water management techniques, including the construction of dikes, windmills, and canals.
– Early Canal Development
The history of canals in the Netherlands dates back to the Middle Ages (roughly 500–1500 AD). Early canals were primarily constructed for drainage and irrigation purposes, allowing agricultural land to be cultivated in marshy areas. These canals also facilitated local trade by connecting villages and towns, enhancing economic activities.
– The Golden Age and Expansion of Canals
The Dutch Golden Age (17th century) marked a significant turning point in the development of canals. During this period, the Netherlands experienced economic prosperity, driven by trade, shipping, and colonial expansion. Major cities such as Amsterdam, Utrecht, and Leiden expanded their canal systems to accommodate growing populations and facilitate trade.
2. The Amsterdam Canal Ring
– Construction and Design
The most famous canal system in the Netherlands is the Amsterdam Canal Ring (Grachtengordel), built in the 17th century. The construction of these canals began in 1613 and continued until the end of the century. The design consisted of a series of concentric canals, with the Herengracht, Prinsengracht, and Keizersgracht forming the main waterways.
– Purpose and Functionality
The Amsterdam canals were primarily designed for practical purposes: managing water levels, providing transportation for goods and people, and protecting the city from flooding. The canals also served as an essential part of the city’s drainage system, allowing excess water to flow away from the urban center.
– Architectural and Cultural Significance
The Amsterdam Canal Ring is not only a feat of engineering but also a UNESCO World Heritage site. The elegant canal houses lining the waterways reflect the wealth and status of the merchants who built them. Today, the canals are integral to the city’s identity, attracting millions of tourists each year and offering scenic boat tours.
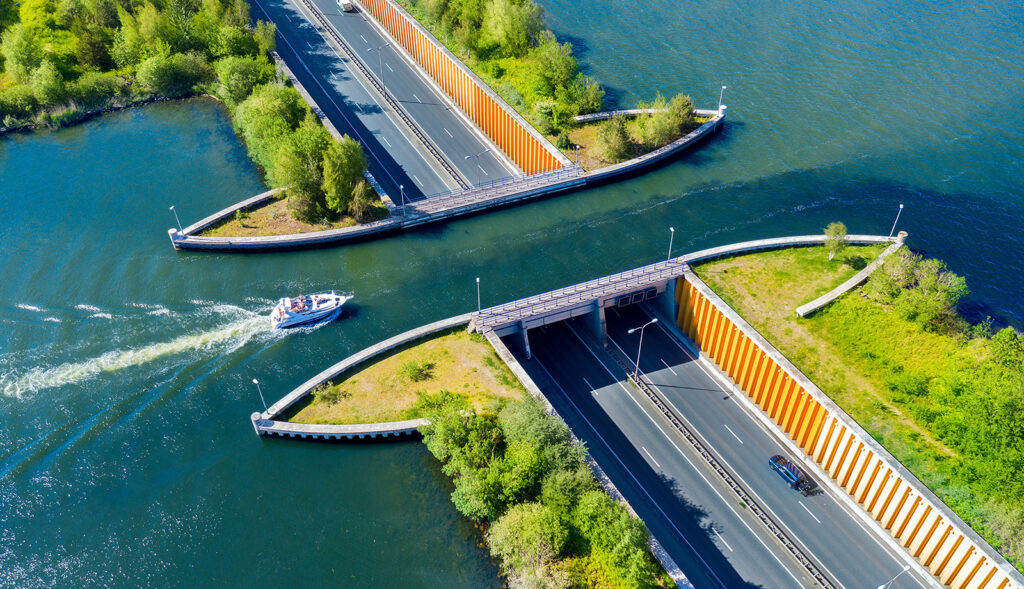

3. The Role of Canals in Trade and Economy
– Facilitating Trade
Canals played a pivotal role in facilitating trade in the Netherlands, connecting inland cities with the North Sea. The transportation of goods via waterways was cheaper and more efficient than overland transport, allowing Dutch merchants to thrive. The canals became crucial arteries for the transport of commodities such as grains, textiles, and spices.
– Economic Impact on Cities
Major cities in the Netherlands developed around their canal systems. For instance, cities like Utrecht and Rotterdam expanded their canal networks to enhance their trade capabilities. The growth of these cities was closely linked to their ability to manage water effectively and facilitate commerce.
A day train from Amsterdam can take you to Switzerland where you can enjoy the Swiss Alps. Here is everything you need to know about the Swiss Alps.
4. Modernization and Challenges
– Industrialization and Canal Use
In the 19th century, with the advent of industrialization, the use of canals evolved. Although railroads began to dominate transportation, canals remained vital for the movement of bulk goods, such as coal and agricultural products. The Netherlands invested in modernizing its canal systems, ensuring their relevance in an industrialized economy.
– Environmental Challenges
In recent years, the Dutch canal systems have faced environmental challenges, including pollution and water management issues. Climate change has heightened concerns about rising sea levels and increased rainfall, leading to more significant flooding risks. The Dutch government has implemented measures to maintain and improve water quality while ensuring the continued functionality of canals.
– Preservation Efforts
The canals are not only crucial for transportation and trade but also hold historical and cultural significance. Preservation efforts are underway to maintain the integrity of the canal systems while adapting them to modern needs. This includes initiatives to enhance water quality, promote biodiversity, and restore historical features.
Canals in the Netherlands – Beauty of the Country
The history of canals in the Netherlands is a fascinating story of ingenuity, adaptation, and resilience. From their early origins as drainage and irrigation channels to their current status as cultural and economic lifelines, the canals have profoundly shaped Dutch society. They remain a vital part of the nation’s identity, reflecting its history, engineering prowess, and commitment to effective water management. As the Netherlands faces modern challenges related to climate change and urbanization, the legacy of its canals will continue to play a crucial role in shaping its future.